Core values and organizational culture in driving organizational excellence
Core values and organizational culture in driving organizational excellence
Core values and organizational culture in driving organizational excellence
Author : Professor Nattapat Lopraditpong
Peter Drucker, the father of modern management, once said, "Culture eats strategy for breakfast," emphasizing that even if an organization's ideas and strategies are excellent, they become meaningless if the organizational culture is toxic and unsupportive. Core values act as guiding principles to instill focus, unity, and shared beliefs among individuals in the organization. They promote consistent behavior throughout the organization, establishing a common foundation for thinking and practices to achieve uniform and regular performance.
The benefits of having strong core values, as compiled by the author, include:
- Fundamental Role in Cultivating a Positive Organizational Culture: Core values are crucial in fostering a positive organizational culture.
- Inspire Motivation and Foster Pride: They generate motivation and pride among all members, creating a sense of unity.
- Aligning Behavior: Core values help align the behavior of individuals in the organization toward a common direction.
- Assisting Decision-making: They aid in decision-making and prioritizing important matters within limited resources.
- Utilized in Recruitment, Retention, and Development: Core values are used in selecting, attracting, retaining, and developing personnel suitable for the organization's goals, strategies, and tasks.
- Performance Evaluation: They contribute to evaluating individual and organizational performance.
- Conflict Reduction and Stimulating Innovation: Core values reduce internal conflicts during critical decision-making and stimulate innovation and improvement.
- Image Building and Customer Perception: They shape the organization's image and perception in the eyes of customers and external stakeholders, attracting the target customer group in the future.
Many organizations establish core values without fully understanding the purpose or end up selecting attractive but irrelevant words that do not connect with the organization's mission. The challenge lies in turning these values into actionable strategies. Some organizations display core values prominently, while others may treat them as opportunities for employee giveaways or annual outings. Some even use core values as a basis for selecting leaders, despite these leaders exhibiting behaviors contrary to the stated values.
In summary, core values play a pivotal role in shaping organizational culture and driving the organization towards excellence when implemented and integrated effectively into daily practices and decision-making processes.
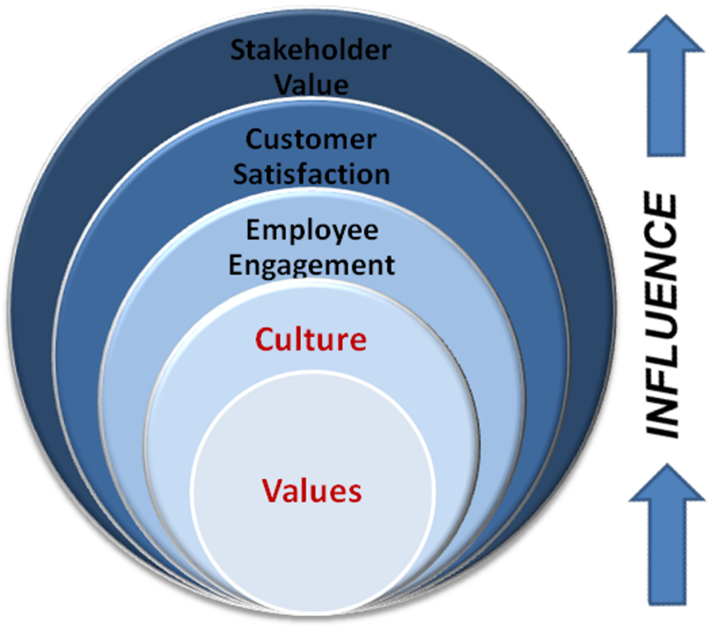
Having good core values and organizational culture promotes employee commitment, leading to the achievement of "successful work, happy people" or "satisfied individuals, successful work." This is considered a critical driver of employee engagement, as satisfied and committed employees tend to work to their full potential, dedicating themselves to achieving results and ensuring customer satisfaction. This, in turn, contributes to the organization's overall success, creating value for stakeholders, shareholders, society, and the community. The cycle continues as satisfied employees positively impact customers, leading to the fulfillment of organizational goals and creating a positive impact on all involved parties in the long run.
The Importance of Core Values and Organizational Culture in Organizational Management towards Excellence:
In a consulting project, the author had the opportunity to exchange perspectives with the top leader of a public company with a market capitalization exceeding one trillion baht. The insights gained highlighted the significance of establishing core values and a strong organizational culture. The following observations were made:
- Decision-making in Small Enterprises: In small enterprises with a few employees and simple business operations, having a single leader making decisions might seem appropriate. This leader, like a knowledgeable elder, can effectively decide on various matters. However, as the organization grows, this approach may no longer be suitable.
- Challenges in Medium Enterprises: In medium-sized enterprises, where the workforce expands to hundreds or thousands, and the customer base grows, relying solely on a single leader may become impractical. Leaders cannot know everything, necessitating the introduction of a management system. This includes setting strategies, translating plans into actions, and implementing key performance indicators (KPIs) to track success.
- Management Systems in Large Enterprises: As enterprises become large, with thousands of employees, diverse branches, and a vast customer base, even a well-designed management system may fall short if the organization lacks shared goals, essential beliefs, and a unified organizational culture.
In summary, the growth of an organization poses challenges to traditional top-down decision-making. Small enterprises may thrive with a single decision-maker, but medium and large enterprises require robust management systems to ensure consistent operations. However, regardless of size, an organization must instill shared goals, essential beliefs, and a unified culture among its members to thrive collectively.
Picture 1.2 Driving organizational culture along with strategy 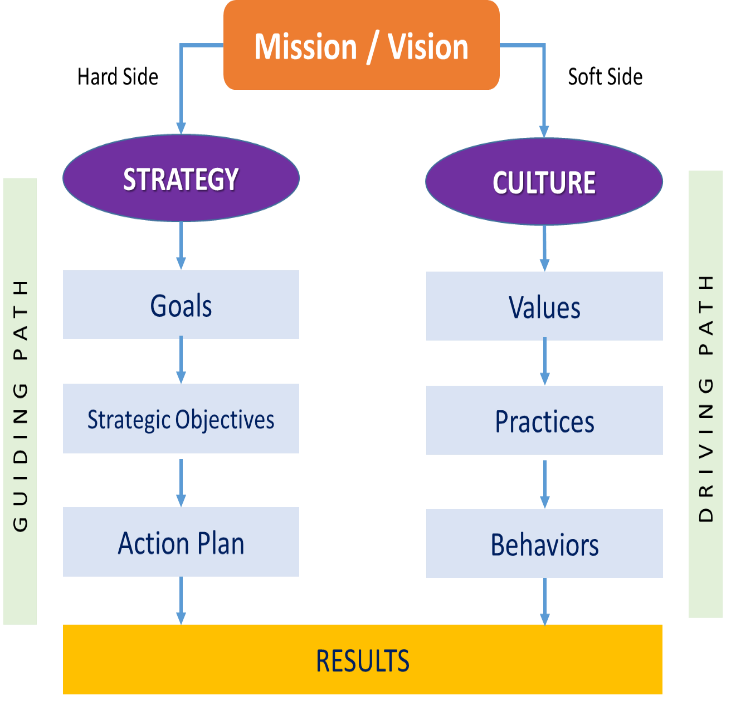
The Management Insights on Driving Organizational Excellence: This senior leader emphasizes the key to driving an organization towards its vision, mission, and objectives lies in effectively managing both the "hard-side" and "soft-side" aspects concurrently. Managing the hard-side involves strategic planning, objectives, plans, systems, standards, and key performance indicators (Guiding Path). On the other hand, managing the soft-side involves molding the thoughts and beliefs of individuals within the organization to share common goals, significant principles, and regular behaviors that evolve into desirable habits (Driving Path).
The Thailand Quality Award, which recognizes organizational excellence, highlights the importance of core values deeply embedded in the organization. These values serve as the foundation for integrating critical operations and requirements for practices under a results-oriented focus. Organizations that excel and endure often share similar fundamental concepts, as outlined in the 11 principles:
- Systems perspective
- Vision-driven leadership
- Customer excellence focus
- Employee focus
- Adaptability and resilience
- Success focus
- Management for innovation
- Management by fact
- Social responsibility
- Ethics and transparency
- Delivering value and results
For further understanding of these principles and the meaning of core values towards excellence, readers are encouraged to explore the National Quality Award criteria. When organizations are seeking or reevaluating their core values, they can consider the synthesized values provided in the list, which have been systematically developed and proven through the Baldrige National Quality Award. This involves studying organizations that have demonstrated excellence and sustainability, providing insights into the fundamental beliefs or core values of these outstanding organizations.
It's common for organizations to misunderstand the process of defining organizational core values, often taking the acronym of the organizational unit and selecting aspirational words with matching initials. The suggested approach is to conduct a thorough analysis of the philosophy, goals, mission, vision, and strategies of the organization. Questions such as "What important values should be instilled in the organization to drive desirable behaviors regularly?" can guide the establishment of core values.
For example, in a hospital setting, core values could include "Patient-Centered" to emphasize prioritizing patients, "Teamwork" to promote interdisciplinary collaboration, and "Risk-Concern" to highlight the importance of risk management. Ultimately, the goal is to create a set of core values that fosters a culture of continuous improvement, consistency, and excellence within the organization.
AUAC Model (Awareness-Understanding-Acceptance-Commitment) for Cultivating Organizational Culture:
Picture 1.2 Driving organizational culture along with strategy
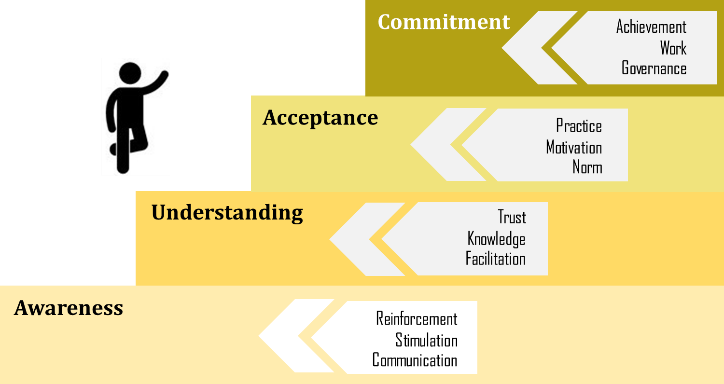
One approach to fostering strong organizational values is through the AUAC model, which stands for Awareness, Understanding, Acceptance, and Commitment. The process unfolds as follows:
- Awareness:
- Initiate by creating awareness among all personnel about the organizational values.
- Conduct various activities such as online and offline communication, producing public relations materials for dissemination, setting high-level executives as positive examples, and declaring commitments/policies.
- The goal is to generate awareness about organizational values.
- Understanding:
- Promote understanding among personnel regarding the significance and impact of organizational values on both the organization and individuals.
- Implement activities such as defining desired and undesired behaviors, conducting competitions for exemplary organizational values, accumulating points for desirable behaviors, organizing promotion campaigns, training sessions, competitions, and recognition.
- The aim is to ensure a clear understanding of the meaning of each value and its translation into tangible behaviors.
- Acceptance:
- Once personnel accept and begin adapting their behaviors according to the expected values, follow-up assessments are often conducted to determine the level of compliance.
- Some organizations include organizational values as part of employees' core competencies, facilitating systematic and continuous evaluation.
- External assessments may involve surveys from both internal (employees) and external (customers and stakeholders) perspectives.
- Exemplary individuals who are not part of the management team may also contribute to the expansion of organizational culture.
- A continuous and foundational practice of desirable behaviors leads to organizational acceptance.
- Commitment:
- Values become an integral part of organizational success, shared goals, and guiding principles for decision-making at both individual and organizational levels.
- Commitment to values is considered a driving force toward achieving predetermined objectives.
- At this stage, both internal and external stakeholders can clearly sense the organizational culture reflected in everyday interactions.
Steps for Cultivating Organizational Culture Towards Excellence:
The author suggests a straightforward method applicable to all organizations, consisting of the following steps:
- Define Core Values: Start by defining the core values of the organization.
- Team Brainstorming: Gather the management team to articulate and define the meaning of each value, emphasizing significant beliefs related to the mission and goals of the organization.
- Communicate and Define Behaviors: Communicate and define behaviors aligned with the values, translating abstract concepts into clear and graspable actions. Develop indicators reflecting these behaviors for clear assessment.
- Policy Formulation: Formulate policies by top-level executives to promote values seriously and induce widespread adoption.
- Plan and Project Implementation: Develop plans and projects to promote values, involving HR and relevant departments.
- Continuous Monitoring and Improvement: Continuously monitor and assess the effectiveness of activities and initiatives to improve in the subsequent years.
By following these steps, organizations can systematically and consistently build and reinforce a positive organizational culture aligned with their core values.
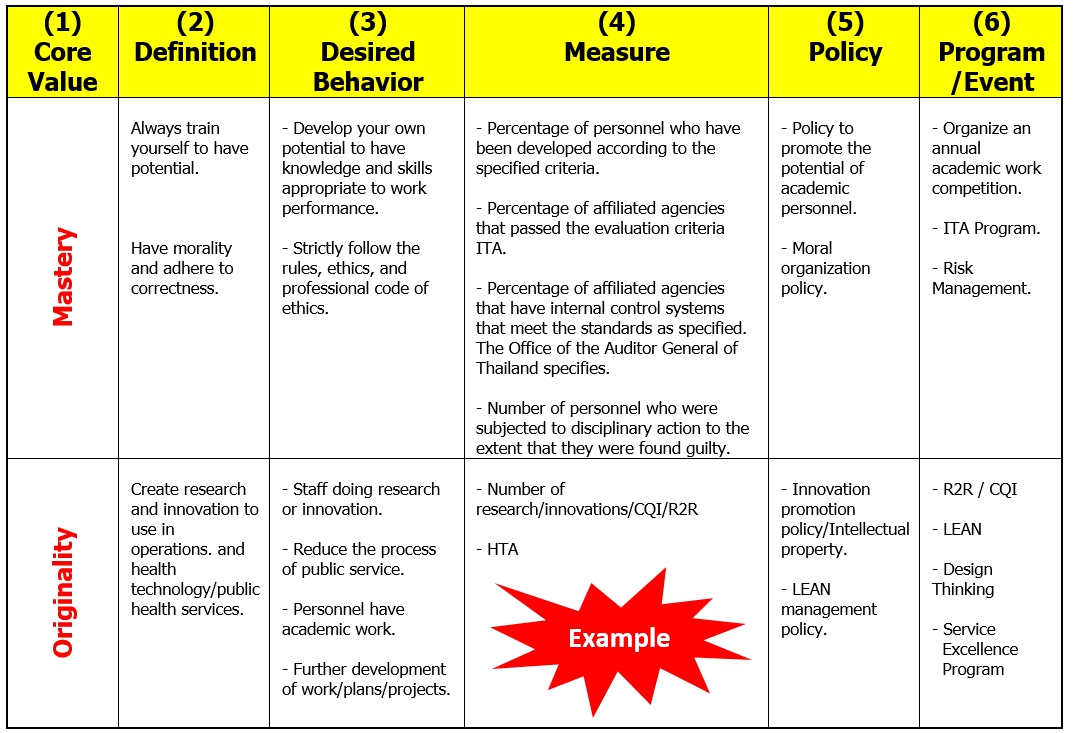
Picture 1.4 Guidelines for driving organizational values and culture
******************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************************
ค่านิยม (Core Value) และวัฒนธรรมองค์กร (Culture) กับการขับเคลื่อนองค์กรสู่ความเป็นเลิศ
Peter Drucker บิดาแห่งการบริหารยุคใหม่เคยกล่าวไว้ว่า “วัฒนธรรมองค์กรกัดกินกลยุทธ์เป็นอาหารเช้า” (Culture eats strategy for breakfast) เพราะแม้ว่าความคิดและกลยุทธ์ขององค์กรจะเลิศล้ำเพียงใดก็ตาม หากวัฒนธรรมองค์กรเป็นพิษ ไม่เสริมส่ง กลยุทธ์นั้นก็ไร้ความหมาย ถูกวัฒนธรรมกลืนกินไปอย่างน่าเสียดาย
ค่านิยมเป็นเสมือนหลักคิดที่จะทำให้คนในองค์กรมี “Focus” ทำให้เกิด “Unity” ในความเชื่อที่ดี มีเป้าหมายร่วมกัน ทำให้เกิดการปฏิบัติตามพฤติกรรมที่พึงประสงค์ เป็นอันหนึ่งอันเดียวกันทั่วทั้งองค์กร สร้างบรรทัดฐานทางความคิดและแนวปฏิบัติให้เกิดความสอดคล้องไปในทางเดียวกันเพื่อให้เกิดการปฏิบัติอย่างสม่ำเสมอ สร้างพลังแห่งการขับเคลื่อนสู่เป้าหมายแห่งความสำเร็จขององค์กร ประโยชน์ของการมี Core Values ที่เข้มแข็ง เท่าที่ผู้เขียนรวบรวมได้ ประกอบด้วย
- ค่านิยมเป็นรากฐานที่สำคัญในการเสริมสร้างวัฒนธรรมองค์กรที่ดี
- สร้างขวัญกำลังใจและสร้างความภาคภูมิใจให้ทุกคนในองค์กร เกิดความเป็นอันหนึ่งอันเดียวกัน
- ช่วยให้การประพฤติปฏิบัติของคนในองค์กรสอดคล้องไปในทิศทางเดียวกัน
- ช่วยในการตัดสินใจ และลำดับความสำคัญของสิ่งที่เป็นสำคัญสำหรับองค์กร ภายใต้ทรัพยากรที่จำกัด
- ใช้ในการคัดเลือก ดึงดูด รักษา พัฒนาบุคลากรให้เหมาะสมกับเป้าหมาย กลยุทธ์และงานขององค์กร
- ช่วยในการประเมินผลการปฏิบัติงานทั้งในระดับบุคคลและองค์กร
- ลดความขัดแย้งภายในองค์กร ในกรณีที่ต้องตัดสินใจเรื่องสำคัญ และกระตุ้นให้เกิดนวัตกรรมและการปรับปรุง
- สร้างภาพลักษณ์และการรับรู้ขององค์กรในสายตาของลูกค้าและผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสียภายนอก ดึงดูดกลุ่มลูกค้าเป้าหมายในอนาคต
หลายองค์กร กำหนดค่านิยมขึ้นโดยมิได้เข้าใจวัตถุประสงค์ว่ามีไปเพื่ออะไร หรือมักกำหนดขึ้นโดยการสรรหาคำที่สวยหรูดูดีแต่ไม่ได้เกี่ยวข้องกับพันธกิจองค์กร ไม่รู้ว่ากำหนดแล้วต้องทำอย่างไรต่อ บ้างก็แปะไว้วข้างฝา แล้วบังคับให้ทุกคนท่องจำเหมือนคำขวัญวันเด็ก บ้างก็ถือเป็นโอกาสในการทำเสื้อแจกพนักงาน บ้างก็ใช้เป็นเหตุผลในการพาพนักงานไปสังสรรค์ประจำปีต่างจังหวัด พวกที่อยู่บนเขาก็จะเลือกลงทะเล ส่วนพวกที่อยู่ทะเลจะไปขึ้นเขา แล้วก็ไปทำกิจกรรม Walk Rally จัดงานปาร์ตี้ โดยอ้างว่าเพื่อเสริมสร้างค่านิยมและวัฒนธรรมองค์กร บางองค์กรก็เลือกส่งเสริมค่านิยมโดยกำหนดให้ผู้บริหารเป็นต้นแบบของค่านิยมแต่ละตัว ทั้งๆ ที่ผู้บริหารเหล่านั้นกลับมีพฤติกรรมตรงกันข้ามกับค่านิยมโดยสิ้นเชิง
ภาพ 1.1 การขับเคลื่อนค่านิยม นำไปสู่การสร้างคุณค่า

การมีค่านิยมและวัฒนธรรมองค์กรที่ดี จะเสริมสร้างบุคลากรให้เกิดความผูกพัน ทำให้เกิด “งานได้ผล คนเป็นสุข” หรือ “คนสำราญ งานสำเร็จ” เพราะถือเป็นปัจจัยเสริมสร้างความผูกพัน (Employee Engagement Driver) ที่สำคัญประการหนึ่ง ซึ่งเมื่อบุคลากรเกิดความพึงพอใจและผูกพัน จะปฏิบัติงานเต็มกำลังความสามารถ และทุ่มเทเพื่อให้เกิดผลงานและสร้างความพึงพอใจแก่ลูกค้าตามมา จนทำให้ผลประกอบการองค์กรบรรลุเป้าหมาย สร้างคุณค่าให้กับผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสีย ผู้ถือหุ้น สังคม ชุมชน ต่อไป
ค่านิยมและวัฒนธรรมองค์กร สำคัญต่อการจัดการองค์กรสู่ความเป็นเลิศอย่างไร?
ในโครงการให้คำปรึกษาแนะนำแห่งหนึ่ง ผู้เขียนมีโอกาสได้แลกเปลี่ยนกับผู้นำสูงสุดขององค์กรมหาชนที่มี Market Cap กว่า 1 ล้านล้านบาท ได้มีการแลกเปลี่ยนมุมมองในการสร้าง Core Value and Culture และสรุปได้ดังนี้ ในการบริหารองค์กรขนาดเล็ก (Small Enterprise) ซึ่งมีบุคลากรเพียงไม่กี่คน ธุรกิจไม่ซับซ้อน การที่องค์กรมีผู้นำสูงสุดตัดสินใจเพียงคนเดียว เหมือนเถ้าแก่ที่รู้ทุกเรื่อง ตัดสินใจทุกเรื่อง ดูจะมีความเหมาะสมดี แต่เมื่อองค์กรมีขนาดใหญ่ขึ้น ธุรกิจเติบโต เป็นองค์กรขนาดกลาง (Medium Enterprise) บุคลากรเพิ่มจำนวนขึ้นเป็นหลักร้อย/หลักพัน มีลูกค้ามากขึ้น การบริหารจัดการโดยมีผู้นำสูงสุดตัดสินใจเพียงผู้เดียว อาจไม่เหมาะสมอีกต่อไป ผู้บริหารอาจไม่รู้ทุกเรื่อง จึงจำเป็นต้องอาศัย “ระบบการบริหารจัดการ” เข้ามาช่วย เช่น กำหนดกลยุทธ์เพื่อถ่ายทอดแผนปฏิบัติการสู่การปฏิบัติ โดยมีตัวชี้วัด (KPIs) ติดตามความสำเร็จ มีการออกแบบระบบงานและกำหนดมาตรฐานการปฏิบัติงานเพื่อให้เกิดความคงเส้นคงวาของกระบวนการในการผลิต/บริการ ต้องกำหนดกฏระเบียบข้อบังคับเพื่อเป็นแนวปฏิบัติของคนทั้งองค์กร ลงโทษเมื่อมีผู้ฝ่าฝืน ต่อมาเมื่อองค์กรเติบโตมีขนาดใหญ่ (Large Enterprise) มีบุคลากรเพิ่มขึ้นหลักพัน/หลักหมื่นคน ลูกค้ามากมาย สาขาหลากหลาย ต่อให้ระบบบริหารจัดการถูกออกแบบมาดีเพียงใดก็อาจ “เอาไม่อยู่” หากคนในองค์กรปราศจากการมีเป้าหมายร่วมกัน ขาดหลักคิดความเชื่อที่สำคัญ หรือการหล่อหลอมคนทั้งองค์กรให้มีค่านิยมและวัฒนธรรมองค์กรร่วมกัน
ภาพ 1.2 การขับเคลื่อนวัฒนธรรมองค์กรควบคู่กลยุทธ์

ผู้บริหารท่านนี้ยังกล่าวถึงเคล็ดลับในการขับเคลื่อนองค์กรเพื่อบรรลุเป้าหมายตามวิสัยทัศน์ พันธกิจ และเป้าประสงค์ไว้ว่า Senior Leader ต้องบริหารส่วนที่เป็น Hard-side และ Soft-side ควบคู่กันไปอย่างกลมกลืน โดยการจัดการส่วนที่เป็น Hard-side หมายถึง การกำหนดกลยุทธ์ วัตถุประสงค์ แผนงาน ระบบงาน มาตรฐาน ตัวชี้วัด ฯลฯ (Guiding Path) ส่วนการบริหาร Soft-side หมายถึง การหล่อหลอมความคิดความเชื่อของคนในองค์กรให้มีเป้าหมายร่วมกัน มีหลักคิดที่สำคัญร่วมกัน และประพฤติปฏิบัติเป็นประจำ จนกลายเป็นพฤติกรรมที่พึงประสงค์ (Driving Path)
เกณฑ์รางวัลคุณภาพแห่งชาติ (Thailand Quality Award) ได้กล่าวถึง Core Value ว่าเป็นความเชื่อและพฤติกรรมที่ฝังลึกอยู่ในองค์กร เป็นรากฐานการบูรณาการระหว่างผลการดำเนินการที่สำคัญและข้อกำหนดของการปฏิบัติการภายใต้การมุ่งเน้นผลลัพธ์ ก่อให้เกิดพื้นฐานการปฏิบัติ การป้อนกลับ และความยั่งยืน องค์กรที่เป็นเลิศและยั่งยืนมักจะมีแนวคิดหลักที่คล้ายคลึงกัน 11 ประการ ดังนี้ 1) มุมมองในเชิงระบบ 2) การนำองค์กรอย่างมีวิสัยทัศน์ 3) ความเป็นเลิศที่มุ่งเน้นลูกค้า 4) การให้ความสำคัญกับบุคลากร 5) ความคล่องตัวและความสามารถในการฟื้นตัว 6) การมุ่งเน้นความสำเร็จ 7) การจัดการเพื่อนวัตกรรม 8) การจัดการโดยใช้ข้อมูลจริง 9) การตอบแทนสังคม 10) จริยธรรมและความโปร่งใส 11) การส่งมอบคุณค่าและผลลัพธ์ โดยท่านผู้อ่านสามารถศึกษาเพิ่มเติมเพื่อเข้าใจแนวคิดและความหมายของค่านิยมสู่ความเป็นเลิศได้ในหนังสือเกณฑ์รางวัลคุณภาพแห่งชาติ และหากองค์กรของท่านกำลังมองหาหรือทบทวนค่านิยมองค์กรในอนาคต อาจพิจารณาเลือกจากใน LIST ข้างต้น ซึ่งเป็นค่านิยมที่ผ่านการสังเคราะห์ตกผลึกมาอย่างเป็นระบบ และได้รับการพิสูจน์มาแล้ว เนื่องจากในการพัฒนาเกณฑ์ Baldrige National Quality Award เกิดจาการศึกษาวิจัยองค์กรที่มีความเป็นเลิศและยั่งยืน ผลการศึกษาที่ได้ออกมาก่อนหลักปฏิบัติ หรือเกณฑ์ 7 หมวด (Criteria) และข้อคำถาม (Questions) ก็คือ หลักคิดหรือค่านิยม (Core Values) ขององค์กรที่เป็นเลิศเหล่านั้นนั่นเอง
องค์กรจำนวนมากมักมีความเข้าใจผิดในการกำหนดค่านิยมองค์กร โดยมักยึดเอาตัวอักษรย่อของหน่วยงานเป็นตัวตั้ง แล้วสรรหาคำสระสรวย ให้มีอักษรตัวแรกของคำสอดคล้องกับตัวอักษรย่อของหน่วยงาน เช่น หากอักษรย่อของหน่วยงานคือ FEP ก็กำหนดค่านิยมเป็น Family, Excellence, Professional เป็นต้น โดยมิได้วิเคราะห์จากปรัชญา เป้าหมาย พันธกิจ วิสัยทัศน์ รวมถึงกลยุทธ์ ขององค์กรว่าควรสร้างหลักคิดที่สำคัญอะไรให้เกิดขึ้นกับคนในองค์กร โดยอาจตั้งคำถามว่า เพื่อที่จะขับเคลื่อนองค์กรไปบรรลุเป้าหมายดังกล่าว คนในองค์กร ควรจะมีหลักคิดความเชื่อร่วมกันในเรื่องใดบ้าง เพื่อส่งเสริมให้เกิดการปฏิบัติอย่างเป็นรูปธรรม สม่ำเสมอ หรือกลายเป็นวัฒนธรรมองค์กรที่ดี ยกตัวอย่างเช่น หากเราจะกำหนด Core Value ของโรงพยาบาล บุคลากรควรมีค่านิยมที่สำคัญเรื่องใดบ้าง เช่น Patient Center เพื่อมุ่งเน้นผู้ป่วยเป็นศูนย์กลาง, Teamwork เพื่อส่งเสริมการดำเนินงานแบบสหวิชาชีพร่วมกัน, Risk-concern ให้ความสำคัญกับความเสี่ยง เป็นต้น
AUAC Model (Awareness-Understanding-Acceptance-Commitment)
ภาพ 1.3 AUAC Model

แนวทางหนึ่งในการส่งเสริมค่านิยมให้เป็นวัฒนธรรมองค์กรที่เข้มแข็ง คือ แนวคิด AUAC หรือ Awareness-Understanding-Acceptance-Commitment โดยมีขั้นตอนดังนี้ Awareness เริ่มต้นที่สร้างความตระหนักรู้ให้กับบุคลากรทุกคนว่ามีการกำหนดค่านิยมองค์กร ให้บุคลากรทุกคนรับรู้ว่ามีค่านิยมใดบ้าง จดจำได้ ด้วยกิจกรรมต่างๆ เช่น การสื่อสารทั้งแบบ on-line และ off-line, การผลิตสื่อประชาสัมพันธ์ต่างๆ เพื่อเผยแพร่, การเป็นแบบอย่างที่ดีของผู้บริหารระดับสูง, การประกาศเจตนารมย์/นโยบาย เป็นต้น โดยมีเป้าหมายเพื่อสร้างความตระหนักรู้ในค่านิยมองค์กร Understanding ส่งเสริมให้บุคลากรมีความเข้าใจถึงความสำคัญและผลกระทบของค่านิยมต่อองค์กรและต่อตนเอง ด้วยกิจกรรมในรูปแบบต่างๆ เช่น การกำหนดพฤติกรรม Do & Don’t, การประกวดบุคคลต้นแบบค่านิยมองค์กร, การสะสมคะแนนความดีตามพฤติกรรมพึงประสงค์, การจัดกิจกรรมรณรงค์ส่งเสริมในรูปแบบต่างๆ, การฝึกอบรม, การประกวด, การให้รางวัล ยกย่องชมเชย เป็นต้น Acceptance เมื่อบุคลากรเกิดการยอมรับและเริ่มปรับพฤติกรรมตนเองไปตามค่านิยมที่องค์กรคาดหวัง และมักมีการติดตามประเมินพฤติกรรมที่พึงประสงค์ว่าเกิดขึ้นในระดับใด องค์กรบางแห่งกำหนดค่านิยมองค์กรเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของสมรรถนะหลักของบุคลากร (Core Competency) ทำให้มีการประเมินและพัฒนาอย่างเป็นระบบและต่อเนื่อง บางองค์กรอาจว่าจ้างหน่วยงานภายนอกทำการสำรวจวัฒนธรรมองค์กรทั้งจากมุมมองภายใน (บุคลากร) และมุมมองจากภายนอก (ลูกค้าและผู้มีส่วนได้ส่วนเสีย) รวมถึงการขยายผลวัฒนธรรมองค์กรผ่านบุคคลต้นแบบ (Role Model) ที่ไม่ใช่กลุ่มผู้บริหาร เมื่อวัฒนธรรมองค์กรเกิดการปฏิบัติอย่างเป็นรูปธรรม ต่อเนื่อง และเป็นพื้นฐานของการตัดสินใจ จะนำไปสู่ขั้นสูงสุดคือ Commitment ค่านิยมเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของความสำเร็จ และเป้าหมายร่วมกันขององค์กร และเป็น Guiding Principle ของการตัดสินใจทั้งในระดับบุคคลและองค์กร เป็นแรงขับเคลื่อนสู่การบรรลุเป้าหมายที่ตั้งไว้ ซึ่งในขั้นตอนนี้ ทั้งคนในและนอกองค์กรมักจะสัมผัสได้อย่างชัดเจนในวัฒนธรรมที่แสดงออกโดยบุคลากรในทุกปฏิสัมพันธ์
ขั้นตอนการสร้างวัฒนธรรมองค์กรสู่ความเป็นเลิศ
ผู้เขียนขอนำเสนอวิธีการเสริมสร้างค่านิยมและวัฒนธรรมองค์กรอย่างง่ายๆ ที่ทุกองค์กรสามารถนำไปประยุกต์ใช้ได้ดังนี้ (ภาพ 1.4) เริ่มต้นจากกำหนด Core Value ขององค์กรในขั้นตอน (1) แล้วระดมสมองในทีมบริหารเพื่อนิยาม หรือกำหนดความหมายของค่านิยมแต่ละตัว ในขั้นตอน (2) โดยเน้นการกำหนดหลักคิดความเชื่อที่สำคัญต่อพันธกิจและเป้าหมายขององค์กรเอง ไม่จำเป็นต้องคัดลอกจากพจนานุกรม เมื่อความหมายของค่านิยมแต่ละตัวมีความชัดเจน และเหมาะสมแล้วจึงร่วมกันสื่อสารและกำหนดพฤติกรรมอันพึงประสงค์ หรือที่องค์กรคาดหวังให้บุคลากรประพฤติปฏิบัติในขั้นตอนที่ (3) ซึ่งในขั้นตอนนี้ต้องแปลงจากสิ่งที่เป็นนามธรรมในขั้นตอนก่อนหน้า ให้กลายเป็นพฤติกรรมที่ชัดเจนจับต้องได้ (กึ่งรูปธรรม) พร้อมกับกำหนดตัวชี้วัดที่สะท้อนพฤติกรรมเหล่านั้นและประเมินได้อย่างชัดเจน (เป็นรูปธรรม) เพื่อใช้ในการติดตามประเมินว่าบุคลากรแสดงออกซึ่งพฤติกรรมอันพึงประสงค์มากน้อยเพียงไร อีกทั้งช่วยในการประเมินความสำเร็จของกิจกรรมหรือแนวทางที่องค์กรใช้ในการขับเคลื่อนอีกด้วย
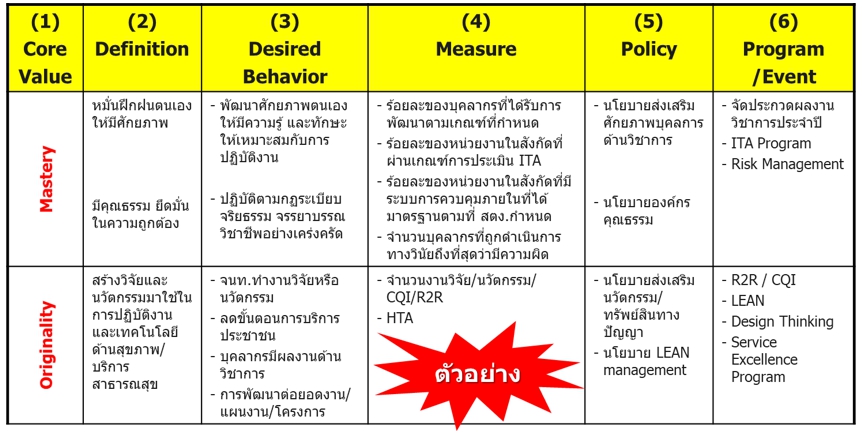
เมื่อกำหนดนิยาม พร้อมพฤติกรรมที่คาดหวังชัดเจนและวัดผลติดตามได้แล้ว ขั้นตอนต่อไปจึงเป็นการกำหนดนโยบายโดยผู้บริหารระดับสูงเพื่อส่งเสริมค่านิยมในขั้นตอนที่ (5) เพื่อแสดงถึงความมุ่งมั่นจริงจังและเกิดการนำไปปฏิบัติทั่วทั้งองค์กร พร้อมกับจัดทำแผนงาน/โครงการส่งเสริมโดยผู้รับผิดชอบในขั้นตอนที่ (6) เช่น ฝ่ายบุคคลร่วมกับหน่วยงานที่เกี่ยวข้อง และเมื่อดำเนินการตามแผนในแต่ละปี ควรมีการติดตามประเมินประสิทธิผลของโครงการ/กิจกรรมต่างๆ และประเมินพฤติกรรมที่พึงประสงค์และตัวชี้วัด ในขั้นตอนที่ (3) และ (4) ว่าเกิดขึ้นจริงหรือไม่ เพื่อปรับปรุงอย่างต่อเนื่องในปีถัดไป ตัวอย่ากรณีศึกษาของโรงพยาบาลแห่งหนึ่งในสังกัดกระทรวงสาธารณสุข มีค่านิยมองค์กร MOPH (Mastery-Originality-People Centered Approach-Humility) ซึ่งทีมผู้บริหารและฝ่ายบุคคลร่วมกันกำหนดและวางแนวทางในการขับเคลื่อนค่านิยมและวัฒนธรรมองค์กรดังภาพ 1.4
ภาพที่ 1.4 แนวทางขับเคลื่อนค่านิยมและวัฒนธรรมองค์กร
04 July 2024
Viewed 596 time

 EN
EN  TH
TH

